Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students should be able to:
i. Explain the concept of carboxylic acids and their structural features.
ii. Identify the different methods for preparing carboxylic acids.
iii. Describe the mechanisms involved in the synthesis of carboxylic acids from various precursors.
iv. Provide examples of carboxylic acids synthesized using different methods.
Introduction
Carboxylic acids, a diverse group of organic compounds, are characterized by the presence of a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. They play a crucial role in various biological processes and are widely used in industrial applications. The synthesis of carboxylic acids is an essential aspect of organic chemistry, as it allows for the preparation of these important compounds with tailored properties.
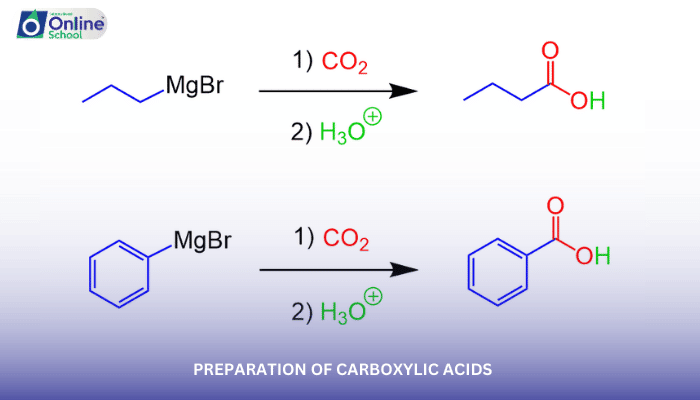
i. Carbonation of Grignard Reagents
Grignard reagents, organomagnesium compounds with the general formula R-MgX, can be reacted with carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce alkylcarboxylic acids. This method, known as the Grignard reaction, is particularly useful for synthesizing carboxylic acids with specific alkyl chains.
ii. Hydrolysis of Nitriles
Nitriles, organic compounds containing a cyano group (-CN), can be hydrolyzed under acidic or alkaline conditions to yield carboxylic acids. This method, known as nitrile hydrolysis, is a versatile approach for synthesizing carboxylic acids from a variety of nitrile precursors.
iii. Oxidation of Primary Alcohols
Primary alcohols, organic compounds with the general formula RCH2OH, can be oxidized to carboxylic acids using strong oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or chromic acid (H2CrO4). This method, known as alcohol oxidation, is particularly useful for the synthesis of aliphatic carboxylic acids.
iv. Oxidation of Aldehydes
Aldehydes, organic compounds with the general formula RCHO, can be oxidized to carboxylic acids using mild oxidizing agents such as silver nitrate (AgNO3) in aqueous ammonia or sodium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) in sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This method, known as aldehyde oxidation, is a convenient route for synthesizing aromatic carboxylic acids.
v. Oxidation of Alkyl Benzenes
Alkyl benzenes, organic compounds with an alkyl group attached to a benzene ring, can be vigorously oxidized using potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or chromic acid (H2CrO4) to produce aromatic carboxylic acids. This method, known as Friedel-Crafts acylation, is particularly useful for the synthesis of benzoic acid derivatives.
The synthesis of carboxylic acids involves a variety of methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. The choice of method depends on the desired carboxylic acid, the availability of starting materials, and the desired reaction conditions. Understanding these synthetic routes is essential for preparing carboxylic acids with specific properties and applications.